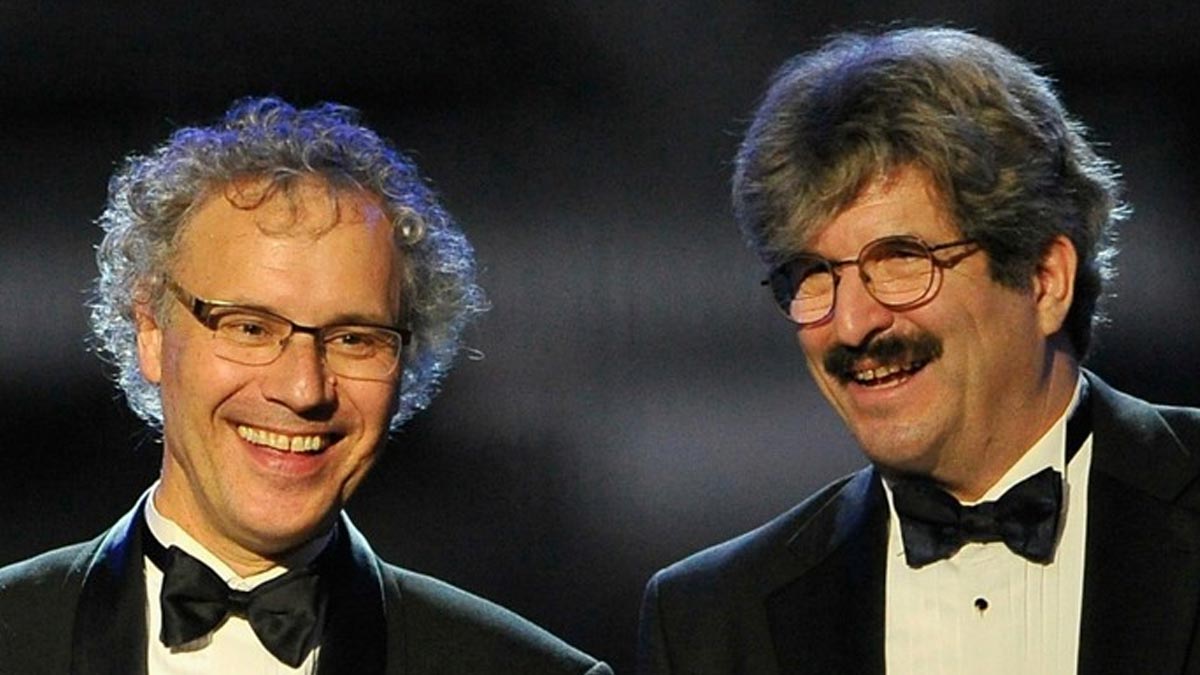
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Medicine has been awarded to two distinguished American biologists, Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun, for their groundbreaking work in the field of genetics. Announced by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, this prestigious award recognises their pivotal discovery of microRNA and its critical function in regulating gene expression following transcription. The Nobel Assembly underscored that their research is “proving to be fundamentally important for how organisms develop and function.”
The Importance of MicroRNA in Gene Regulation
Ambros and Ruvkun’s research has shed light on a tiny yet immensely significant molecule known as microRNA. These molecules, composed of small strands of RNA, play a crucial role in controlling gene activity within various types of cells. Despite the fact that every cell in an organism possesses the same genetic material, the diverse functions of different cell types—such as muscle cells versus nerve cells—are made possible through gene regulation mechanisms. This regulation allows cells to selectively activate only the genes required for their specific functions.
The discovery of microRNA has revealed a previously unrecognised method of gene regulation. Prior to their work, the understanding of gene expression was largely centred around proteins that bind to DNA or RNA. However, Ambros and Ruvkun’s research demonstrated that microRNAs act as key regulators, influencing how genes are expressed by targeting messenger RNAs (mRNAs) for degradation or inhibition of translation. This discovery has fundamentally altered our understanding of genetic control and has paved the way for further research into the intricacies of gene regulation.
Also Read: Gurugram Sees Surge In Dengue Cases With 90 Reported; Health Officials Urge Precautions
Implications for Development and Disease
The implications of this discovery extend far beyond basic biology. Understanding how microRNAs function is essential for comprehending developmental processes in organisms, including humans. By regulating gene expression, microRNAs play a vital role in determining cell fate, guiding cellular differentiation, and orchestrating the complex interactions that underlie development.
Moreover, the study of microRNA has significant implications for the understanding and treatment of various diseases. Aberrant microRNA expression has been linked to a range of conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders. Researchers are now investigating how manipulating microRNA levels could lead to novel therapeutic strategies. For instance, restoring the function of specific microRNAs that may be downregulated in diseases could provide new avenues for treatment.
Also Read: ICMR’s Groundbreaking Study Unveils Foods Fueling India’s Diabetes Epidemic
A Legacy of Discovery
Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun’s contributions to the field of genetics exemplify the essence of scientific discovery: a combination of curiosity, perseverance, and innovative thinking. Their work has opened up a new field of research in molecular biology, inspiring countless scientists to explore the roles of microRNAs in health and disease. As the implications of their findings continue to unfold, the potential for future breakthroughs in medical science remains vast.
In awarding the Nobel Prize to Ambros and Ruvkun, the Nobel Assembly has not only honoured their individual achievements but has also highlighted the importance of basic research in unravelling the complexities of life. Their discovery of microRNA serves as a reminder of how fundamental scientific inquiries can lead to profound advancements in our understanding of biology and medicine.
Bottomline
The recognition of Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun with the 2024 Nobel Prize in Medicine underscores the significance of their pioneering research on microRNA and its essential role in gene regulation. Their findings have not only transformed our understanding of genetic control but have also set the stage for new approaches in disease treatment and prevention. As the scientific community celebrates this achievement, it is clear that the impact of their work will resonate for generations to come, guiding future research and inspiring new discoveries in the realm of biology and medicine.

